
Unlock The Power Of The Cloud. Embrace Cloud-Native
Cloud-native deployments are designed to fully utilize the advantages of cloud environments.
Key characteristics include:
- Microservices: Decomposing applications into smaller, independently deployable services.
- Containers: Packaging applications and dependencies into portable units (Docker is common).
- Orchestration (often Kubernetes): Automating container deployment, scaling, and management.
- DevOps and CI/CD: Continuous integration/continuous deployment pipelines for rapid development and release cycles.
Securing Beyond Boundaries
At Kraft Software Solutions, we are committed to offering high-quality Cybersecurity Services to protect your digital presence and valuable assets. We take a proactive approach to cybersecurity, aiming to identify and address vulnerabilities before they turn into threats. Our support is available 24/7 to resolve any issues and ensure the security of your systems.

Capabilities
- Security Consulting- Strategic insights for robust cybersecurity strategies.
- Application & Network Security Evaluation- In-depth analysis to identify vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing- Simulated attacks to assess system defenses.
- Technical support –OS and Software- OS and Software Continuous support for a secure operating environment.
- Robustness and Vulnerability Scan- Proactive scanning for vulnerabilities and robustness testing.
- Risk Advisory- Expert guidance on risk mitigation and compliance.
- Manages Incident Response and Digital Forensics- Swift response and forensic analysis in case of security incidents.
Deployment approaches when migrating to cloud-native
Lift and Shift
Taking an existing application and running it in the cloud with minimal changes (often on virtual machines). This is required when we need a quick move to the cloud, often as a first step before modernization.
Refactoring (or Re-architecting)
Breaking down an application into microservices, making it more scalable and cloud friendly.
This can be used when the organizations want to maximize cloud benefits (resiliency, scalability), and existing architecture is a bottleneck.
Cloud-Native Greenfield Development
Building an application from scratch using cloud-native principles (microservices, containers, etc.).
This approach is used when you are starting a new project and want the full cloud-native advantages.
These applications are designed to fully leverage the scalability, resilience, speed, and innovation potential offered by the cloud.
Core Cloud Service Models
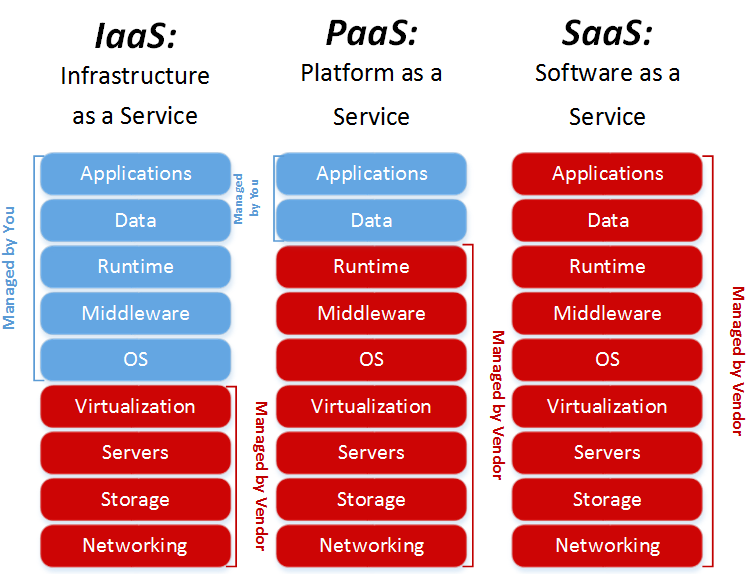
IaaS
Organizations migrate from On-premise to IaaS as this eliminates the need to purchase, upgrade and maintain the physical servers and data centers. When there is a requirement for increasing or decreasing resources based on need, we can scale them accordingly. It has a very good approach to disaster recovery as it enables easy replication of infrastructure and data to different cloud regions. IaaS also deploys servers closer to your users in different geographic regions for reduced latency. This way when an organization spends less time focusing on the infrastructure, it ultimately focus on development and innovation.
PaaS
PaaS provides middleware services and runtime environments necessary for building and running applications laying the path for simplified development and deployment. The pre-configured environments and tools streamline the process and shorten release cycles. PaaS platforms have an enhanced scaling feature that handles the incoming spikes in traffic efficiently. With all the available services, organizations will have reduced operational overhead.
SaaS
The SaaS provider manages the infrastructure, software updates, security, and backups, freeing up your IT team. These applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for distributed systems and remote work. Another feature is quick deployment, as there are no lengthy setups required. It is highly scalable, and the organization can easily add or remove users as needed without worrying about the hardware requirements.
Key Considerations
Choosing the right cloud service model involves balancing the following:
- Control vs. Convenience: IaaS offers more control, SaaS offers the most convenience. PaaS is in between.
- Technical Expertise: IaaS requires the most in-house management skills.
- Legacy Systems: Some may be better suited for IaaS (lift and shift), while refactoring may be necessary to fully leverage PaaS and SaaS benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What services are included in Cloud Managed Services?
Cloud Managed Services oversee the entire lifecycle of core cloud services, employing CI/CD DevOps principles for efficient implementation
Are your Cloud Managed Services compatible with multi-cloud environments?
Our Cloud Managed Services support multi-cloud environments, allowing businesses to harness the strengths of various cloud providers.
What tools are used for Cloud Managed Services?
We leverage automation, monitoring, and security tools to ensure a robust and secure cloud environment.
How can I get started with Cloud Solutions?
Start your cloud journey with a consultation. We’ll assess your needs and guide you through the adoption process.
 Sampath Kumar Sabbineni (Sam) began his career as a software developer and gained valuable experience in various roles at prominent MNC’s such as Deloitte, Capgemini, and Amway over a span of 13 years. In 2016, he embarked on his entrepreneurial journey by joining Kraft Software Solutions in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and has since expanded globally as a VKraft Software Services with branches in Singapore, India, Indonesia, and The USA. Sam provides a range of innovative Digital Solutions addressing challenges in the Digital Era. His vision is to lead at the forefront of the digital platform, offering products with unique functionalities across diverse sectors, including Healthcare, Insurance, Banking, Retail, Logistic, Environmental, and Manufacturing.
Sampath Kumar Sabbineni (Sam) began his career as a software developer and gained valuable experience in various roles at prominent MNC’s such as Deloitte, Capgemini, and Amway over a span of 13 years. In 2016, he embarked on his entrepreneurial journey by joining Kraft Software Solutions in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and has since expanded globally as a VKraft Software Services with branches in Singapore, India, Indonesia, and The USA. Sam provides a range of innovative Digital Solutions addressing challenges in the Digital Era. His vision is to lead at the forefront of the digital platform, offering products with unique functionalities across diverse sectors, including Healthcare, Insurance, Banking, Retail, Logistic, Environmental, and Manufacturing.